
The carbon-sulfur bond is a chemical bond that forms between a carbon atom (C) and a sulfur atom (S). This bond is commonly found in a variety of organic compounds, particularly in the field of organic chemistry and biochemistry. The carbon-sulfur bond is key in several important classes of molecules, including thiols, sulfides, and sulfonic acids. Its strength, polarity, and reactivity can vary depending on the specific molecules and the functional groups involved. But what makes the carbon-sulfur bond unique? How does it compare to other bonds, and why is it so important in chemical processes? Let’s take a closer look.
The carbon-sulfur bond is typically covalent, meaning the carbon and sulfur atoms share electrons. However, the electronegativity difference between carbon (2.55) and sulfur (2.58) is very small, leading to a bond that is only slightly polar. This makes the carbon-sulfur bond less polar than, for example, the carbon-oxygen bond in alcohols or ethers. Despite this, sulfur atoms are larger and more polarizable than oxygen atoms, which contributes to the bond’s unique properties.
The bond strength of the carbon-sulfur bond is generally lower than that of the carbon-oxygen bond, making it more reactive in certain chemical reactions. Additionally, sulfur’s ability to form multiple bonds and its role as a nucleophile in organic chemistry makes the carbon-sulfur bond important in a wide range of synthetic processes. Is c-s polar or nonpolar?
Is c-s polar or nonpolar? To understand the polarity of the carbon-sulfur bond, we can look at the following aspects: bond strength, electronegativity difference, and the behavior of the bond in chemical reactions.
Molecular Structure: The carbon-sulfur bond is typically represented as a single bond in most organic compounds, where the carbon atom is bonded to sulfur in various configurations. Sulfur’s larger atomic size and its electron-donating characteristics influence the reactivity of molecules containing this bond.
Dipole Moment: Although the electronegativity difference between carbon and sulfur is small, sulfur is still slightly more electronegative, meaning the sulfur atom will attract the shared electrons more than the carbon atom. This creates a slight dipole moment within molecules containing a carbon-sulfur bond, but the effect is less pronounced compared to bonds involving more electronegative atoms like oxygen or nitrogen.
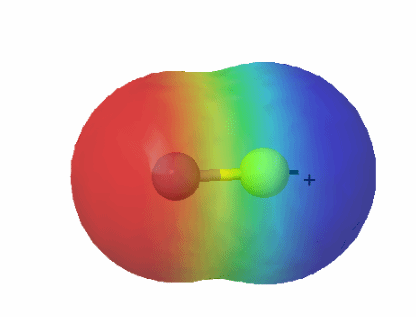
Electronegativity: The electronegativity values of carbon and sulfur are quite close, but sulfur is slightly more electronegative than carbon, which influences the distribution of electron density in the bond. This results in a mild polarity that affects the reactivity and solubility of compounds containing carbon-sulfur bonds. The C-S bond is generally nonpolar due to similar electronegativities of carbon and sulfur.
The carbon-sulfur bond plays a critical role in a variety of chemical and industrial applications. Its unique characteristics make it essential in several fields, including organic synthesis, materials science, and medicine.
| Carbon-Sulfur Bond Information | |
| Bond Type | Covalent |
| Electronegativity Difference | 0.03 (Carbon 2.55, Sulfur 2.58) |
| Bond Strength | Moderate |
| Bond Length | Varies depending on the compound |
| Compound | Polarity | Applications |
| Methanethiol (CH₃SH) | nonpolar | Used in flavoring agents and as an industrial solvent |
| Dimethyl sulfide (CH₃SCH₃) | Slightly polar | Used in food industry for flavor and as a solvent |
| Thiophene (C₄H₄S) | nonpolar | Used in organic electronics and as a chemical intermediate |
 |
 |
 |