
|
Sodium Phosphate Monobasic Monohydrate, with the chemical formula NaH2PO4·H2O, has the CAS number 10049-21-5. It appears as a white crystalline powder with no odor. The basic structure of Sodium Phosphate Monobasic Monohydrate consists of one sodium atom, two hydrogen atoms, one phosphorus atom, and four oxygen atoms. This compound is highly soluble in water. It is important to handle Sodium Phosphate Monobasic Monohydrate with caution as it may cause irritation to the eyes, skin, and respiratory system. Ingestion or inhalation of this compound may also cause gastrointestinal disturbances. It is recommended to use appropriate protective equipment when handling Sodium Phosphate Monobasic Monohydrate.
Applicable Fields
Laboratory Research: Sodium Phosphate Monobasic Monohydrate is commonly used in laboratory research as a buffering agent. Its purpose in this field involves maintaining a stable pH level in various experimental procedures. The mechanism of action of Sodium Phosphate Monobasic Monohydrate as a buffering agent involves its ability to resist changes in pH by accepting or donating hydrogen ions.
Pharmaceuticals: This compound is also utilized in the pharmaceutical industry. Sodium Phosphate Monobasic Monohydrate can be found in various medications and formulations. Its purpose in this field may involve acting as an excipient, a pH adjuster, or a stabilizer, depending on the specific pharmaceutical product.
Storage
Conditions: Store in a cool and dry place.

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
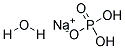
|

|
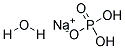
|
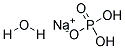
|

|

|

|

|