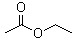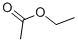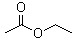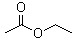Ethyl acetate (CAS 141-78-6) is a colorless liquid with a fruity odor. It has a basic structure consisting of an ethyl group attached to an acetate group. This chemical is highly soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol and ether, but only slightly soluble in water. Ethyl acetate has a boiling point of 77.1°C and a melting point of -83.6°C. It is a volatile compound, meaning it evaporates easily at room temperature.
Ethyl acetate exhibits several physical properties. It is a flammable liquid and should be handled with caution. It has a density of 0.897 g/cm3 and a vapor pressure of 73 mmHg at 20°C. The chemical properties of ethyl acetate include its ability to undergo esterification reactions, where it can react with alcohols to form esters. It is also known to react with strong bases and acids.
Applicable Fields
Paints and Coatings: Ethyl acetate is commonly used as a solvent in the production of paints, varnishes, and lacquers. Its mechanism of action involves dissolving the resin and pigment components, allowing for easy application and drying of the coating.
Adhesives: In the adhesive industry, ethyl acetate serves as a solvent for various types of adhesives. It helps to dissolve the adhesive components, allowing for proper bonding of materials. The mechanism of action involves the evaporation of ethyl acetate, leaving behind a strong and durable adhesive bond.
Pharmaceuticals: Ethyl acetate is used as a solvent in the extraction and purification of pharmaceutical compounds. It can selectively dissolve certain compounds, separating them from impurities. This mechanism of action is commonly employed in the production of herbal extracts and active pharmaceutical ingredients.
Storage Conditions
Store in a cool, dry place.