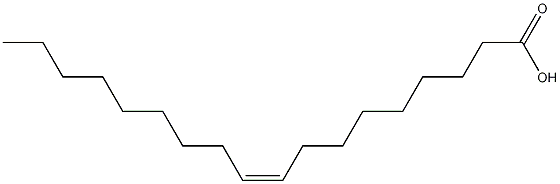
Oleic acid (CAS 112-80-1) is a fatty acid that is commonly found in various natural sources such as animal and vegetable fats and oils. It is a colorless to pale yellow liquid with a characteristic odor. The basic structure of oleic acid consists of a long hydrocarbon chain with a carboxylic acid group (-COOH) at one end. It is insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol and ether.
Oleic acid exhibits several physical properties. It has a melting point of approximately 13.4°C and a boiling point of around 360°C. The density of oleic acid is about 0.895 g/cm3. It has a high viscosity and a refractive index of 1.461. Chemically, oleic acid is classified as an unsaturated fatty acid due to the presence of a double bond between carbon atoms in its hydrocarbon chain.
Oleic acid is known for its various chemical properties. It undergoes typical reactions of carboxylic acids, such as esterification, oxidation, and saponification. It can form esters with alcohols, undergo oxidation to form peroxides, and react with bases to form salts called oleates. Oleic acid is also susceptible to degradation through processes such as hydrolysis and polymerization.
Applicable Fields
Oleic acid finds applications in several fields:
1. Cosmetics: In the cosmetic industry, oleic acid is used as an emollient and emulsifying agent. It helps to soften and moisturize the skin, making it a common ingredient in lotions, creams, and other skincare products.
2. Pharmaceutical: Oleic acid is utilized in the pharmaceutical industry as a drug delivery agent. It can enhance the absorption of certain drugs through the skin and mucous membranes, making it useful in transdermal and topical formulations.
3. Food Industry: Oleic acid is present in various food products and is commonly used as a cooking oil. It is also used as an ingredient in the production of margarine, spreads, and other food products. Oleic acid contributes to the flavor and texture of these products.
Mechanism of Action
Oleic acid's mechanism of action varies depending on its application:
1. Cosmetics: In cosmetics, oleic acid acts as an emollient by forming a protective barrier on the skin, reducing water loss, and improving skin hydration. It also functions as an emulsifying agent, helping to stabilize the formulation and improve its texture.
2. Pharmaceutical: In pharmaceutical formulations, oleic acid enhances drug absorption by increasing the permeability of the skin or mucous membranes. It can solubilize lipophilic drugs and facilitate their penetration into the target tissues.
3. Food Industry: In the food industry, oleic acid contributes to the flavor and texture of food products. It acts as a lubricant, providing a smooth mouthfeel, and can also function as a preservative by inhibiting the growth of certain microorganisms.
Storage Conditions
Store in a cool, dry place.