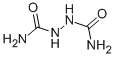
Biurea (CAS 110-21-4) is a white crystalline solid that is commonly used in various industrial applications. It has a basic structure consisting of two urea molecules linked together. Biurea is highly soluble in water, resulting in a clear solution. It has a melting point of approximately 190-195°C and a boiling point of around 220-225°C. This compound is stable under normal conditions and does not react with air or water. Biurea is odorless and non-toxic, making it suitable for different uses.
Applicable Fields
Biurea has several applications in different fields:
Agriculture: Biurea is used as a nitrogen fertilizer. It releases nitrogen slowly, providing a long-lasting source of nutrients for plants. The mechanism of action involves the gradual hydrolysis of biurea, releasing urea and ammonia, which can be absorbed by plants.
Chemical Industry: Biurea is utilized as a crosslinking agent in the production of resins and polymers. It reacts with other compounds, forming strong chemical bonds and increasing the strength and durability of the final product.
Research and Development: Biurea is used as a starting material for the synthesis of various organic compounds. Its unique structure and reactivity make it a valuable building block in organic chemistry.
Storage Conditions
Store in a cool, dry place.